Osteochondrosis is the most difficult form of the degenerative-half-strewable spine, which is based on the defeat of an intervertebral disk, with subsequent deformations of the body of neighboring vertebrae, reduced ligasical appliances and the inclusion of the pathological process of nervous systems and blood vessels.
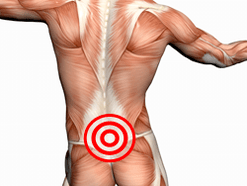
One of the most common forms of osteochondrose is the osteochondrose of the lumbar region, or more precisely, a lumbosachlorn spine.Many - both men and women - meet with pain in the back in the lower back, Sacrum, lower extremities, caused by different types of lumbar osteochondrose and its complications.Among the reasons for temporary disability and disability, this disease occupies one of the first places.
The course of the disease is chronic, usually with periods of deterioration.The most often worsens the osteochondrose of the lumbar lineme cranes and transferring weights, hypothermia, stress and injuries.
Osteochondrosis of lumbar spine - causes, mechanism of phenomena and development
There was no unambiguous cause of osteochondrose, the disease is considered polyphab.The most popular theory is, according to which the cause of osteochondrosis of the spine is constantly made of muscle or hypotension of muscle, which leads to the overload of the vertebrae, and, ultimately, the result is the result of the result of osteochondrose.
The cause of premature aging interverters can also be endocrine and metabolic disorders, hereditary predisposition to develop osteochondrose, autoimmune disorders and microtracia.The negative role of visceral, ie associated with internal bodies, pathologies of the development of osteochondrose of the spine, has also been proven.A significant role in disease development belongs to negative inheritance.The contribution of hereditary factors on the occurrence of lumbar osteochondrose is about 60%, the rest refers to the factors of adverse external influence on the spine.
Factors that contribute to the development of osteochondrosis and in lumbar and other parts of the spine are very numerous.The main one: improper posture, hypodynamia, muscle overvoltage in the lumbar area as a result of constant weight spending, endocrine and somatic disease, spinal injury, emotional stress, changed changes, bad nutrition.Under the influence of these factors in the spine structures, the processes of dehydration and circulation, arthritis and subclusion in small joints, bone growth and disks - the hernias gradually increases.
The most obvious causes of lumbar osteochondrosis are most often considered a seated lifestyle and injury back.Therefore, the risk group primarily includes those people whose profession is directly connected to the load on the back.This is a very wide range of professions - seller and waiters, surgeons and teachers - all who are forced to spend most working hours.The risk group includes buildings and drivers, as well as athletes who, which, in the nature of activities, are created by large loads on the spine.In addition, drivers, various office workers, developers - or those who have a job mostly sitting, and who suffer from hypodynamia, suffer from osteochondrose lumbar.
Symptoms of osteochondrose lumbar spine
InLumbar OsteochondrosisA painful sensation of various nature is possible.This one can either be a pain that occurs with an extended seat or after sleep, as well as sharply recording, causing the most uncomfortable position and not allowing the opportunity to correct.Pain is killed with nervous roots, irritation of their own nerves of the spinal pillar, edema and irritation of muscles and ligaments located in the Inervation zone of the lumbar spine.
Sirome pain can be caused by the compression of radical structures (radiculopathy), spinal cord compression, spinal cord damage due to damaged blood supply due to pushing, narrowing and vein (vascular milen).
The reason for compression can be: protrusion and hernia of intervertebral discs, spondylolistz (sliding forwards forward compared to the basic), osteophyte growth and crispy tissues in segment rarely.As a resultOsteochondrose of the lumbar regionThe rain leads to the tears of channels through which cerebrospinal nerves or vascular structures pass, and under certain conditions (clumsy movement, physical activity, the unsuccessful turn of the body, etc.), can occur in compression.Compression of nerve structures leads to different pain syndromes, muscular cramps.The blood vessel compression causes blood supply violation - ischemia of an organ that begins to feed from this vessel or artery.
Clinical syndromes of osteochondrose lumbar spine
The clinical picture for lumbar osteochondrosis was determined by the complex of the symptoms of vertebrae (the change of statics and the dynamics of lumbar spine) and accompaniment of symptoms, which are implyed as a violation of the function of neurological and vascular structures in the lumbosakral region of the spine.
Vertebral syndromes of lumbar osteochondrose
With lumbar osteochondrose, vertebrae syndrome characterizes the following complex symptoms:
- Violation of the configuration of the functional-anatomical spine segment: adheres to straightening or (less often) increased lordosis, scoliosis or lordoscoliosis;
- Violation of mobility in the lumbar area, reducing the volume of movements, muscular-tonic imbalances caused by tensioning deep and superficial multi-human muscles;
- Local pain and pain with active and passive movements, which cause reflex tonic muscle tension;
- Breach of spring motor functions and intervertebral disk and, in general, segment of the engine vertebrae;
- Local pain (increased sensitivity) of bone-ligamental spine structures in the affected area (pain during palpat, local (regional) vertebrae and / or life-pain syndrome).
It is important to note that the lumbar department is always observed with osteochondrome.The presence of signs of Meolopathy, radiculopathy and myeloradiculopathy without obvious clinical and morphological signs of vertebrae syndrome, usually requires more on the patient's field for the primary ("nesorester") of the nervous system.
Extroovertebral (reflex and compression) Syndromes for osteochondrose lumbar spine
Extrovern syndromes are divided into two large groups: reflex and compression.
Reflex syndromesThey are compressed too much and are caused by irritation of the nerve root receptor that appear from the spinal channel through the intervertebral holes.Irritation can cause intervertebral hernia, bone growth, as well as vascular disorders (edema, deterioration of blood circulation) and inflammation.In some cases it leads to intense pain, not just locally, but also during the nerve at a distance of irritation - thus-wereked "reflected pain", reflected pain can be short and stupid Dugin.In the inervic zone of the injured nerve, vegetative disorders (combustion, goosebumps, damaged sensitivity) are possible.Myofascial aches are possible - muscular spasm, which leads to limiting movement.
Reflex syndromes include Lumbago ("Shift") in the acute disease development and lumbalgia with a subacute or chronic course.
Compression syndromes are syndromes that occur as a result of compression, violations of nerves, blood vessels, spinal cords in the area of lumbar spinal segments.Compression syndromes for osteochondrose Department of Lumbusacratra are divided into radicular and vascular-brown.A special case of compression syndrome is Frenolopathy - a breach of the spinal cord.
Released syndromes (radiculopathy) are usually due to the discouragement, causing violation of cerebrospinal roots.Radicular symptoms arising in this case match the level of the affected vertain segment.The most commonly influenced the roots of L4-S1.
Vascular-brown neurological disorders are caused by the kile compression on the spine and the root artery that passes.At the same time, "paralytic ishias" can develop catastrophically, characterized by peripheral paresis or paralysis of the muscle foot rates.In such cases, the appearance of motor disorders is accompanied by the disappearance of pain.
Even these are more difficult neurological events caused by violation of blood to the spinal cord due to damage to the radio capacular spinal arteries.At the same time, chronic micropolarbalies of myelopathy develops, usually at the level of lumbar thickening of the spinal cord.
The most unfavorable version of the lumbar vertical radicular syndromes is a compression of the "horse's tail" - so-the cudal syndrome.It is most often caused by a drop-down brader kilina disc, which grip all the roots at the level of the affected segment.
What is the osteochondrose of the lumbar spine?What are his symptoms?How to treat osteochondrose of Lumbar?
Clinical classification of osteochondrose lumbar regions.Stonechondrose degree
The classification of lumbar osteochondrosis according to the degrees is used for the systematic characteristics of the clinical manifestations of the disease.This classification systematically describes the symptoms of the disease and starts from the moment the patient has pain.
1 degree of osteochondrose
Occurs when an intervertebral disk appears caused by sharp motion or overvoltage.It is manifested by sudden pain, in the spine, the feeling of passing electricity appears, the muscles are reflective tense.
2 degrees osteochondrose
The second degree can be manifested in the form of symptoms of interpretable protuberance and spine instability.Chronic pain that increases on the gym.Remission intervals and worsening are replaced.The cervical region is characterized by neck pain, increasing after a long stay in one position, headache, pain in hand, shoulder pain, periodic discomfort or stiffness in the fingers.For the lumbar region - lower back pain, pain in glutel-end, periodic pain in the cross hid, a common fatigue in their legs.
3 degrees osteochondrose
It is manifested in the form of the intervertebral disk symptom (a hurry of the affected nerve, the symptoms of the intervertebral hernia (in the heads of the thoracic hearts, breathing, breathing difficulties; in the lumbar region: renal disease,Gastrointestinal tract, violations in the genital area, stiffness or weakness in their legs).
4 degrees osteochondrose
It is generally accepted that the fourth level of osteochondrose begins when the kila is no longer manifested, the manifestations of the disease can be reduced, but the symptoms of spinal instability or their complete fixation or their complete fixation are still compared to their complete fixation.The events of the rags of the rook bodies (osteophytes) can be joined to them, which can emphasize and spinal nerves or overlap the spinal channel (secondary stenosis of spinal channel) and squeeze the spinal cord (spinal cord).In addition, the fourth degree includes the consequences of the surgical intervention if the hernia immediately removed (various types of innovation, paresis, inflammation).
Treatment of osteochondrose lumbar spine
With the first acute lower back pain, it is necessary to advise with a doctor to establish a diagnosis to exclude the attack of renal colic, appendicitis or any other disease that requires emergency medical care.
If the cause of the pain in the back is known, such a deterioration of osteochondrose of the lumbar spine, it is necessary to maximize the load on the spine.It is necessary to observe a vacation for 3 to 7 days - sometimes only it can significantly reduce the pain.But to accelerate recovery, it is necessary to accurately, that is, efficient, treatment.It should be encouraged by their own protective and health processes in the human body.Treatment should take into account the localization of the lesion, phase of disease, functional state of the body and its individual systems.The surgical treatment of this disease is listed only in very difficult cases.Different methods of conservative treatment of osteochondrose are most often used.
Conservative treatment of lumbar osteochondrose
Conservative methods of treatment are, above all, medicine treatment.In order to reduce pain as well as to reduce inflammation, which is often the cause of vertebrae syndrome, non-asteoid anti -infalmator drugs (NSAIDs) in the form of tablets or - in the form of injections.Sometimes, after injection, analgesics, the pain is calmed and does not continue when it lasts a healing substance.This means that it was possible to break a vicious circle in which pain leads to muscle cramps, and muscle tensions, in return, improves pain.However, if pain is long, it is important to remember that NSAIDs usually have different side effects and with extended use can cause unwanted complications - reduction in the number of leukocytes in the blood, complications from the gastrointestinal tract.
Sedatives (soothing) agents for improving the general condition of patients are often prescribed within 1-3 weeks, as well as small dose of antidepressants.With the osteochondrose of the lumbar spine, if necessary, the blockade of the Novokaine was produced.Recently, antikonvulsuls drugs began to use successfully to relieve pain.
In order to reduce compression syndromes, manual therapy, traction treatment (spine) and surgery are used in special cases.
During the weakness of the properties of a vegamental and consistent spine device, the use of fastening devices - trifles, collars, overflows, etc. is recommended.However, only a limited time can be used for fastening devices, as the muscle weakening is noticed.And the patients with spinal osteochondrose are extremely important in the future to strengthen their own muscle corsets.
After removing acute symptoms, the task of creating muscle fixation comes first in the first place, and then encourage the process of regeneration of damaged structures.To do this, use therapeutic gymnastics, reflexology, massage.To do this, use ChondroProtectors.Like medications that improve the state of blood vessels (angioprotectors), vitamins, primarily groups B, calcium preparations that improve the state of bone tissue.
For the treatment of osteochondrose, spine are widely used physiotherapy procedures.They reduce tissue pain and edema, improve blood circulation and encourage muscle fixation.Procedures can be combined, alternative.Such methods of physiotherapy treatment such as:
- Daranslation of the affected area of the back and affected limbs;
- electrophoresis;
- Laser radiation low - technology;
- ultrasound;
- Exposure to the magnetic field;
- Thermal procedures.
In the conditions of sanatorium, mud, ozoker, paraffin applications, radon, sulfide, hydrogen Sumlfide, turpentine and other bathing areas are successfully used;
It must be borne in mind that for the development of full regeneration, it takes a rather long period of time, under favorable circumstances that occur in the sixth month.Therefore, treatment needs long.It should be performed by a combined way, ie combined medications with physiotherapy and physiotherapy exercises.